Cancers Associated With Overweight And Obesity
In young adults, the six obesity-related cancers that increased in incidence in were multiple myeloma, colorectal, uterine corpus, gallbladder, kidney, and pancreatic cancer.
Contents

Simply put, obesity is the result of taking in more calories through your diet than you are burning through physical activity.
The reasons for this calorie imbalance vary from person to person. It can sometimes be linked to the genes we were born with, or our environments, as well as our individual behaviour and choices. And some drugs and diseases can also contribute to weight gain.
Most people can reach and stay within a healthy weight range by eating healthily, eating smaller amounts and becoming more active. Visit our tips and advice on keeping a healthy weight.
How could obesity lead to cancer?
The link between obesity and cancer risk is clear. Research shows that excess body fat increases your risk for several cancers, including colorectal, post-menopausal breast, uterine, esophageal, kidney and pancreatic cancers.
What’s less clear is exactly how being obese increases that risk. Experts believe it’s largely due to the inflammation caused by visceral fat – the fat that surrounds your vital organs.
“The problem with excessive visceral fat is that it affects certain processes in your body. This includes how your body manages hormones, like insulin and estrogen,” says Karen Basen-Engquist, Ph.D., professor in Behavioral Science at MD Anderson.
“All of this can lead to an increased cancer risk by affecting how and when cells divide and die,” she says.
What is known about the relationship between obesity and cancer?
Which Cancers Are Affected?
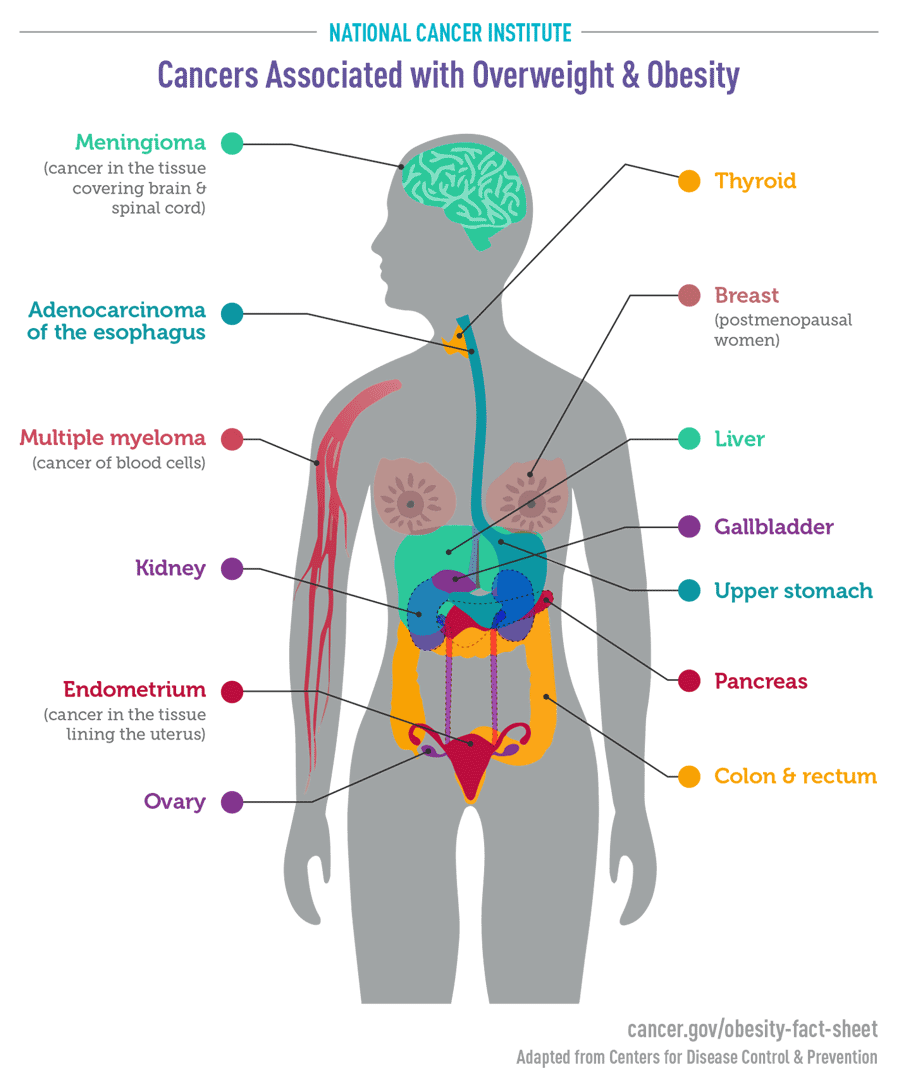
Research has shown that many types of cancer are more common in people who are overweight or obese, including cancers of the breast (in women after the menopause), bowel, womb, oesophageal (food pipe), pancreatic, kidney, liver, upper stomach (gastric cardia), gallbladder, ovarian, thyroid, myeloma (a type of blood cancer), and meningioma (a type of brain tumour).
This list includes 2 of the most common types of cancer – breast and bowel cancers – and 3 of the hardest to treat – pancreatic, oesophageal and gallbladder cancers.
There is consistent evidence that higher amounts of body fat are associated with increased risks of a number of cancers (, including:
Vital Signs: Trends In Incidence Of Cancers Associated With Overweight And Obesity Answers
1.Endometrial cancer:
2.Esophageal adenocarcinoma:
3.Gastric cardia cancer:
4.Liver cancer:
5.Kidney cancer:
6.Multiple myeloma:
Meningioma: The risk of this slow-growing brain tumor that arises in the membranes surrounding the brain and the spinal cord is increased by about 50% in people who are obese and about 20% in people who are overweight
7.Pancreatic cancer:
8.Colorectal cancer:
A higher BMI is associated with increased risks of colon and rectal cancers in both men and in women, but the increases are higher in men than in women
9.Gallbladder cancer:
10.Breast cancer:
Among postmenopausal women, those who are obese have a 20% to 40% increase in risk of developing breast cancer compared with normal-weight women . The higher risks are seen mainly in women who have never used menopausal hormone therapy and for tumors that express hormone receptors. Obesity is also a risk factor for breast cancer in men (23).
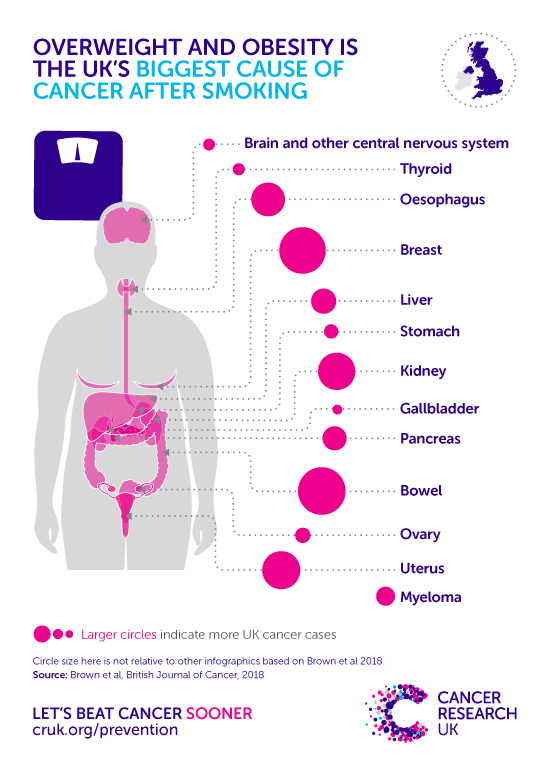
How being overweight causes cancer

Extra fat in the body can have harmful effects, like producing hormones and growth factors that affect the way our cells work. This can raise the risk of several diseases, including cancer. More than 1 in 20 cancer cases in the UK are linked to being overweight or obese.
Dr Vishnubala, a GP in York, talks about how obesity can cause cancer, who is at risk, and how to lose weight.
What is my risk of developing cancer if I’m overweight or obese?
The risk is greater the more weight you gain and the longer you are overweight for. But that doesn’t mean the damage is done. You can help stack the odds against cancer by avoiding gaining more weight. And evidence is growing to show risk can start to go back down with weight loss. Plus the best ways to lose weight for most people are by eating healthily and moving more which on their own reduce cancer risk.
If you are thinking of losing weight and think you need support, a personal trainer,your doctor or nurse will be able to help.
Belly fat has harmful effects
When too much fat is carried around the belly, it can do even more damage. So-called ‘apple’ shapes are linked to bowel, kidney, oesophageal, pancreatic, and breast cancers.
It isn’t clear exactly why this is, but it could be to do with how quickly certain chemicals from fat can get into the blood.
A healthy body weight is important for children as well as adults
One in five children are overweight or obese before they begin primary school, and one in three children are overweight or obese by the time they leave.
Obese children are more likely to grow into obese adults, and obese adults are more at risk of cancer. It is possible overweight children may be at increased risk of cancer as adults, regardless of what they grow up to weigh, but the evidence isn’t clear.
By encouraging your children to lead a healthy lifestyle, you can help them keep a healthy body weight as a child as well as later on in life.


